Table of Contents
- What is Sheet Metal Gauge Chart
- Aluminum Gauge Chart
- Popular Sheet Metal Materials
- Sheet Metal Applications
- Mild Steel Gauge Chart
- Galvanized Steel Gauge Chart
- Stainless Steel Gauge Chart
- Copper Gauge Chart
- Sheet Metal Fabrication
- Steel Sheet Metal Tolerances
- Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Gauge Chart Thickness
- Sheet Metal Surface Finishes
- Brass Gauge Chart
- Sheet Metal Weldings
- Stainless Steel Sheet Weight
- How are Sheet Metal Gauges Used?
- Sheet Metal Advantages and Disadvantages
Understanding the Sheet Metal Gauge Chart
A sheet metal gauge chart is a crucial tool in the metalworking industry, used to determine the thickness of sheet metal. The gauge number corresponds inversely to the thickness; the higher the gauge number, the thinner the metal sheet. This relationship between gauge and thickness helps manufacturers select the appropriate material for specific applications, balancing factors such as strength, weight, and cost.
Aluminum Gauge Chart for Accurate Thickness Selection
Selecting the correct aluminum gauge is vital for projects requiring specific mechanical properties. Knowing the exact thickness ensures proper functionality and durability. For instance, aerospace components often demand thicker sheets for structural integrity, whereas packaging materials might require thinner sheets to reduce weight and cost.
Using an aluminum gauge chart, engineers can match the required thickness with the corresponding gauge number, optimizing both performance and budget. For example, a gauge 7 aluminum sheet measures approximately 3.665 mm (0.1443 inches), making it suitable for heavy-duty applications like industrial equipment.
Looking for the Best Quality Sheet in Various Sizes? Explore the Sheet Metal Gauge Chart in mm and Inches Below
Aluminum Gauge Chart
| Gauge No. | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MM | 3.665 | 3.264 | 2.906 | 2.588 | 2.305 | 2.053 | 1.628 | 1.291 |
| Inches | 0.1443 | 0.1285 | 0.1144 | 0.1019 | 0.09074 | 0.08081 | 0.06408 | 0.05082 |
| Gauge No. | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 | – |
| MM | 1.024 | 0.812 | 0.644 | 0.511 | 0.405 | 0.321 | 0.255 | – |
| Inches | 0.0403 | 0.03196 | 0.02535 | 0.0201 | 0.01594 | 0.01264 | 0.01003 | – |
Popular Sheet Metal Materials
| Stainless Steel | Pre-plated Steel | Cold Rolled Steel | Copper/Brass | Aluminum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400 Series | 300 Series | Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel | Smooth Finish Hot Rolled Steel | Electrolytically Tough Pitch (ETP) | Grade 1100: Low Strength |
| Grade 410: Less Corrosion Resistance, Heat Treatable | Grade 316: Corrosion-Resistant, Maintains Strength at High Temperatures | Â | Available in 1018, 1008 Alloys | Cartridge Brass (Alternative) | Grade 3003: Stronger, Corrosion-Resistant |
| Grade 430: Used Where Corrosion Resistance is Not Required | Grade 304: Widely Used, Less Corrosion-Resistant | Â | Â | Â | Â |
| Â | Good Formability and Weldability | Â | Â | Â | Â |
Applications of Sheet Metal
- Architecture
- Structural Components
- Housings
- Enclosures
- Manufacturing
- Cabinets
- Construction
- Automation
Thickness and Gauge Values Vary by Material
The gauge value serves as a standardized measure for determining sheet thickness, expressed either in inches or millimeters. Higher gauge numbers correspond to thinner sheets, while lower gauge numbers indicate thicker sheets. Non-ferrous metals, such as copper and aluminum, use a different gauge system, measured in ounces per square foot.
Explore Standard Gauges for Sheet Metal Charts Across Various Materials Below
Mild Steel Gauge Chart
| Gauge no. | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MM | 4.554 | 4.175 | 3.797 | 3.416 | 3.038 | 2.656 | 1.897 |
| Inches | 0.1793 | 0.1644 | 0.1495 | 0.1345 | 0.1196 | 0.1046 | 0.0747 |
| Gauge no. | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 |
| MM | 1.518 | 1.214 | 0.911 | 0.759 | 0.607 | 0.454 | 0.378 |
| Inches | 0.0598 | 0.0478 | 0.0359 | 0.0299 | 0.0239 | 0.0179 | 0.0149 |
Galvanized Steel Gauge Chart
| Gauge no. | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MM | 4.269 | 3.891 | 3.51 | 3.1318 | 2.753 | 1.9939 | 1.6129 |
| Inches | 0.1681 | 0.1532 | 0.1382 | 0.1233 | 0.1084 | 0.0785 | 0.0635 |
| Gauge no. | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 |
| MM | 1.31 | 1.005 | 0.853 | 0.701 | 0.551 | 0.474 | 0.398 |
| Inches | 0.0516 | 0.0396 | 0.0336 | 0.0276 | 0.0217 | 0.0187 | 0.0157 |
Stainless Steel Gauge Chart
| Gauge No | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MM | 4.365 | 3.968 | 3.571 | 3.175 | 2.778 | 1.984 | 1.587 |
| Inches | 0.17187 | 0.15625 | 0.14062 | 0.125 | 0.10937 | 0.07812 | 0.0625 |
| Gauge No | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 |
| MM | 1.27 | 0.9525 | 0.7937 | 0.635 | 0.476 | 0.396 | 0.3175 |
| Inches | 0.05 | 0.0375 | 0.03125 | 0.025 | 0.01875 | 0.01562 | 0.0125 |
Copper Gauge Chart
| Gauge No. | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MM | 4.572 | 4.191 | 3.759 | 3.404 | 3.048 | 2.769 | 2.108 | 1.651 |
| Inches | 0.18 | 0.165 | 0.148 | 0.134 | 0.12 | 0.109 | 0.083 | 0.065 |
| Gauge No. | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 | |
| MM | 1.245 | 0.889 | 0.711 | 0.559 | 0.457 | 0.356 | 0.305 | |
| Inches | 0.049 | 0.035 | 0.028 | 0.022 | 0.018 | 0.014 | 0.012 |
Sheet Metal Fabrication
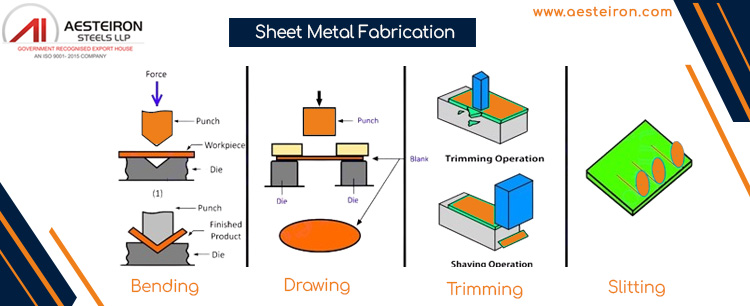
| Bending | Cutting | Punching | Forming |
|---|---|---|---|
Creates bend lines and applies force to achieve the desired angle |
Choice of method depends on thickness, material type, and required precision |
Done by punching press or CNC machine |
Shaping the metal into desired forms
|
| Welding | Finishing | Inspection | Â |
Ensures parts are securely attached |
Protects against corrosion |
|
 |
Sheet Metal Gauge Chart Size Range: 0/7 SWG to 50 SWG
Steel Sheet Metal Tolerances
| Gauge | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal [in] | 0.1345 | 0.1196 | 0.1046 | 0.0747 | 0.0598 | 0.0478 | 0.0359 | 0.0299 | 0.0239 | 0.0179 | 0.0149 | |
| Max | Size [in] | 0.1405 | 0.1256 | 0.1106 | 0.0797 | 0.0648 | 0.0518 | 0.0389 | 0.0329 | 0.0269 | 0.0199 | 0.0169 |
| Min | Size [in] | 0.1285 | 0.1136 | 0.0986 | 0.0697 | 0.0548 | 0.0438 | 0.0329 | 0.0269 | 0.0209 | 0.0159 | 0.0129 |
Stainless Steel Sheet Metal Gauge Chart Thickness
| Gauge | 12 | 11 | 24 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.109" | 2.78mm | 0.120" | 3.05 mm | 0.025" | 0.64 mm | 0.063" | 1.59mm |
| Thickness Tolerance | ± 0.009 | ± 0.23mm | ± 0.005 | ± 0.003 | ± 0.08mm | ± 0.006 | ± 0.15mm |
| Gauge | 14 | 20 | 18 | 22 |
| Thickness | 0.078" | 1.98mm | 0.038" | 0.95mm | 0.050" | 1.27mm | 0.031" | 0.79 mm |
| Thickness Tolerance | ± 0.007 | ± 0.18mm | ± 0.004 | ± 0.10mm | ± 0.005 | ± 0.13mm | ± 0.004 | ± 0.10mm |
Sheet Metal Surface Finishes
- Annealing
- Galvanized
- Tinning
- Anodizing
- Tempering
Refer to Brass Gauge Thickness in MM
The following brass gauge thickness information is essential for customers due to several reasons:
The thickness of brass directly influences the efficiency of the manufacturing process. For example, excessively thick brass can make it difficult to cut or shape into desired forms. Conversely, very thin brass may be prone to bending and failure under stress.
It determines the structural strength and longevity of the final product. Proper thickness ensures that the component can withstand the intended load and environmental conditions.
It also impacts the overall project cost. Not all parts require high thickness, and excessive thickness can increase production and shipping expenses unnecessarily.
Thin-gauge brass can be damaged by high heat exposure. Therefore, welders take precautions to minimize heat exposure during welding processes.
Brass Gauge Chart
| Gauge No. | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MM | 3.665 | 3.264 | 2.906 | 2.588 | 2.305 | 2.053 | 1.628 | 1.291 |
| Inches | 0.1443 | 0.1285 | 0.1144 | 0.1019 | 0.09074 | 0.08081 | 0.06408 | 0.05082 |
| Gauge No. | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 | |
| MM | 1.024 | 0.812 | 0.644 | 0.511 | 0.405 | 0.321 | 0.255 | |
| Inches | 0.0403 | 0.03196 | 0.02535 | 0.0201 | 0.01594 | 0.01264 | 0.01003 |
Sheet Metal Welding Techniques
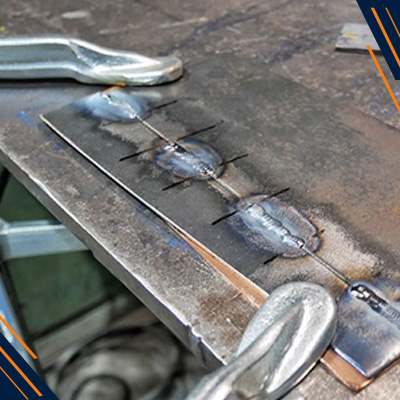

MIG Welding
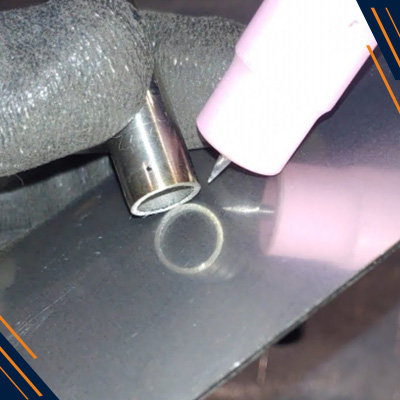

TIG Welding

Laser Welding

Stick Welding

GAS Welding

Plasma Arc Welding
Gauge Sizes Depend on the Weight of Steel, Which is 41.82 Pounds Per Square Foot Per Inch of Thickness
This standard gauge of metal sheets ensures uniformity in thickness, which directly impacts the toughness, longevity, and performance of the final product. A precise gauge selection allows manufacturers to meet design specifications while minimizing unnecessary material usage, leading to cost-effective solutions.
Stainless Steel Sheet Weight
| Weight Per Stainless Steel Sheet | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight KG/M2 | 1.44 | 1.6 | 1.76 | 1.92 | 2.16 | 2.24 | 2.56 | 3.04 | 3.52 | 4 | 4.48 | 5.04 | 6 | 7.04 | 8 | 9.04 | 10 | 72 | 12 | |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.18 | 0.2 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.44 | 0.5 | 0.56 | 0.63 | 0.75 | 0.88 | 1 | .1.13 | 1.25 | 1.38 | 1.5 | |
| Size(mm) | 2500 X 1250 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 11 | 12.5 | 14 | 15.75 | 18.75 | 22 | 25 | 28.25 | 31.25 | 34.5 | 37.5 |
| 2000 X 1000 | 2.88 | 3.2 | 3.52 | 3.84 | 4.32 | 4.48 | 5.12 | 6.08 | 7.04 | 8 | 8.96 | 10.08 | 12 | 14.08 | 16 | 18.08 | 20 | 22.03 | 24 | |
| 3000 X 1500 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 36 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 54 | |
| Weight KG/M2 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 | 32 | 34 | 36 | 40 | 44 | 48 | 52 | 56 | 60 | 64 | |
| Thickness (mm) | 1.75 | 2 | 2.25 | 2.5 | 2.75 | 3 | 3.25 | 3.5 | 3.75 | 4 | 4.25 | 4.5 | 5 | 5.5 | 6 | 6.5 | 7 | 7.5 | 8 | |
| Size(mm) | 2500 X 1250 | 43.75 | 50 | 56.25 | 62.5 | 68.75 | 75 | 81.25 | 87.5 | 93.75 | 100 | 106.25 | 112.5 | 125 | 137.5 | 150 | 162.5 | 175 | 187.5 | 200 |
| 2000 X 1000 | 28 | 32 | 36 | 40 | 44 | 48 | 52 | 56 | 60 | 64 | Welded precision tube,cold drawn welded tube,cold drawn ERW steel tube, welded precision steel tube,precision steel tube,DOM tubing Changzhou Chengxin Metal Products Co., Ltd , https://www.chengxinsteeltube.com | |||||||||