Geographic resources have developed a new training of SOM decomposition on temperature response
[ Instrument Network Instrument Development ] The response of soil organic matter (SOM) to temperature changes not only affects soil nutrient cycling, but also affects terrestrial ecosystem carbon source/sink effects. The temperature sensitivity (Q10) of soil organic matter decomposition is not only one of the core scientific issues of ecology and soil science research, but also a hotspot of global change ecology research. Domestic and foreign scholars have carried out a lot of fruitful research work on the influencing factors or mechanisms of Q10, and there are many related reviews or prospects; however, there have been very few discussions about culture and measurement models.
Traditionally, researchers have widely used the constant temperature culture + intermittent measurement mode (CDM mode); that is, by cultivating the soil by setting 3 to 6 constant temperatures (such as 5, 10, 15, 20, 25oC, etc.), and then in the sky, At the weekly and monthly intervals, the soil organic carbon decomposition rate (Rs) was determined; in the test method, most of the determination was carried out by alkali absorption or gas chromatography, and then Q10 was calculated using the measured Rs and the corresponding temperature. Later, on this basis, some people proposed to improve the soil culture to a continuous temperature change mode, namely continuous temperature change culture + interval test mode (VDM mode). These two classical modes greatly promote the study of temperature response of SOM decomposition, but can not overcome its inherent problems from theory, algorithm and operation (see the original discussion).
In order to overcome the shortcomings of CDM and VDM models, on the basis of summarizing the related research of the predecessors, the research team of the Institute of Geographical Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, He Nengpeng developed a device and technology for continuous variable temperature culture combined with continuous-high frequency soil microbial respiration rate (PRI). -8800), and developed a new mode of continuous temperature change culture + continuous automatic test of Q10 research (figure, VCM mode). VCM mode makes full use of the advantages of continuous variable temperature culture + continuous-high frequency soil microbial respiration measuring device, and realizes continuous temperature-changing culture of soil samples, which basically overcomes the adaptability of soil microorganisms to specific culture temperature and substrate consumption in CDM mode. An important flaw in unevenness. The VCM model develops a continuous-high-frequency soil microbial respiration measurement system that combines the temperature characteristics of the culture process to perform continuous, high-frequency testing of each sample during the rise/lower temperature process. By measuring the microbial respiration rate of soil at more temperatures, the fitting accuracy of Q10 is improved. At the same time, with the support of new equipment, the VCM mode training and testing process is very simple and fast, which is conducive to a large number of sample testing or large-scale networking research.
Based on the theoretical exploration of the advantages and disadvantages of the three models, the research team combined the three models to carry out a multi-point comparative case study. The relevant papers on the advantages and disadvantages of VCM model and the application prospects are recently in the field of soil science. & Biochemistry is officially published online. This paper is a continuation of a large number of researches in the early stage of the team, and provides a methodological study for the future research on the response of SOM decomposition to temperature changes at home and abroad.
Relevant research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31770655, 415711300043), the National Key Research and Development Program (2016YFC0500102), and the Youth Team Project of the Key Laboratory of Ecosystem Observation and Simulation (LENOM2016Q0005).
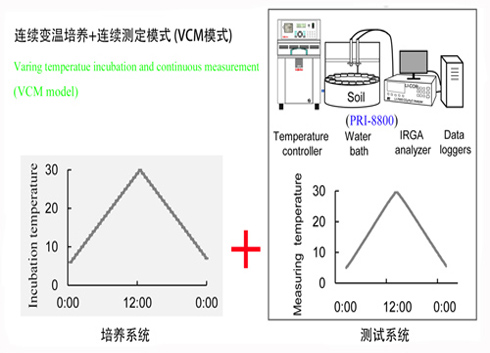
SOM decomposition continuous temperature change response to temperature change + continuous measurement mode (VCM mode)
Small Autoclave,Composite Material Autoclave,Composite Treatment Autoclave,Civil Use Autoclave
JIANGSU OLYMSPAN THERMAL ENERGY EQUIPMENT CO.,LTD , https://www.compositesautoclave.com